Cookies have been the primary way of tracking online users since the dawn of the internet. Many companies in the ad tech space have been heavily relying on the third party cookie to track audiences, target users, and create user identity graphs. However, there will be large changes to this starting on February 4, 2020. Starting on that day, Google will implement SameSite Cookie changes which effectively force everyone to comply with their SameSite Cookie infrastructure.
What is the SameSite cookie?
The SameSite cookie attribute is a format of information exchange where the type of cookie is declared. The cookie can be declared as one of 3 different variables:
- None: Available for 3rd party cookie sharing
- Lax: Allows for cookie sharing among a publisher’s owned sites
- Strict: No cross-site sharing at all
Google SameSite Cookies Changes
- Starts on February 4, 2020
- Will be released concurrently with Chrome 80.
- Currently, the default SameSite cookie attribute is set to “SameSite=None”. Google will change the default to be “SameSite=Lax” when it rolls out the change. This means that developers must consciously set switch their defaults when they change rolls out.
- Currently, non-secure HTTP requests work with “SameSite=None”. All attributes with “SameSite=None” will be invalid if it is not passed via a secure HTTPS request. This means that any publisher that wishes to use third-cookies will have to move to HTTPS if they have not already done so.
Why the Update?
Google is getting more aggressive with SameSite to prevent insecure data sharing across domains and cross-site request forgery (CSRF), which is when hackers manipulate authenticated cookies into taking malicious actions which can lead to a plethora of negative implications.
Possible Results of Cross-Site Request Forgery
- Unauthorized transfer of bank funds
- Damaged client relationships
- Data theft
- Changed passwords
- Malicious social engineering
- Malicious tracking
Cross-Site Request Forgery Example from Imperva
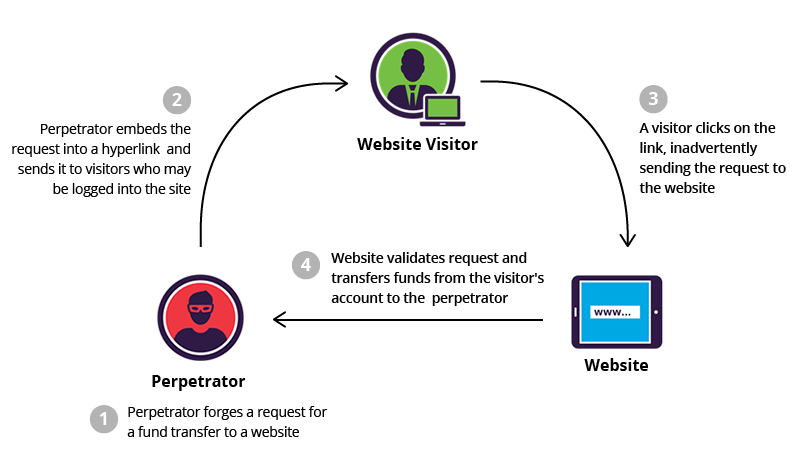
Sources
- https://adexchanger.com/privacy/google-will-limit-cross-site-tracking-in-chrome-by-default-starting-in-february/
- https://digiday.com/media/what-is-chrome-samesite/
- https://web.dev/samesite-cookies-explained/
- https://www.imperva.com/learn/application-security/csrf-cross-site-request-forgery/
You have brains in your head. You have feet in your shoes. You can steer yourself any direction you choose.
— Dr. Seuss



