What is GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) standardizes data protection law across all 28 EU countries and imposes strict new rules on controlling and processing personally identifiable information (PII). It also extends the protection of personal data and data protection rights by giving control back to EU residents. GDPR replaces the 1995 EU Data Protection Directive, and goes into force on May 25, 2018. It also supersedes the 1998 UK Data Protection Act.
There are many essential items in the regulation, including increased fines, breach notifications, opt-in consent and responsibility for data transfer outside the EU. As a result, the impact to businesses is huge and will permanently change the way customer data is collected, stored, and used.
GDPR applies to all organizations holding and processing EU resident’s personal data, regardless of geographic location. Many organisations outside the EU are unaware that the EU GDPR regulation applies to them as well. If an organization offers goods or services to, or monitors the behavior of EU residents, it must meet GDPR compliance requirements.
What countries are affected by GDPR?
GDPR affects all countries within the European Union (EU).
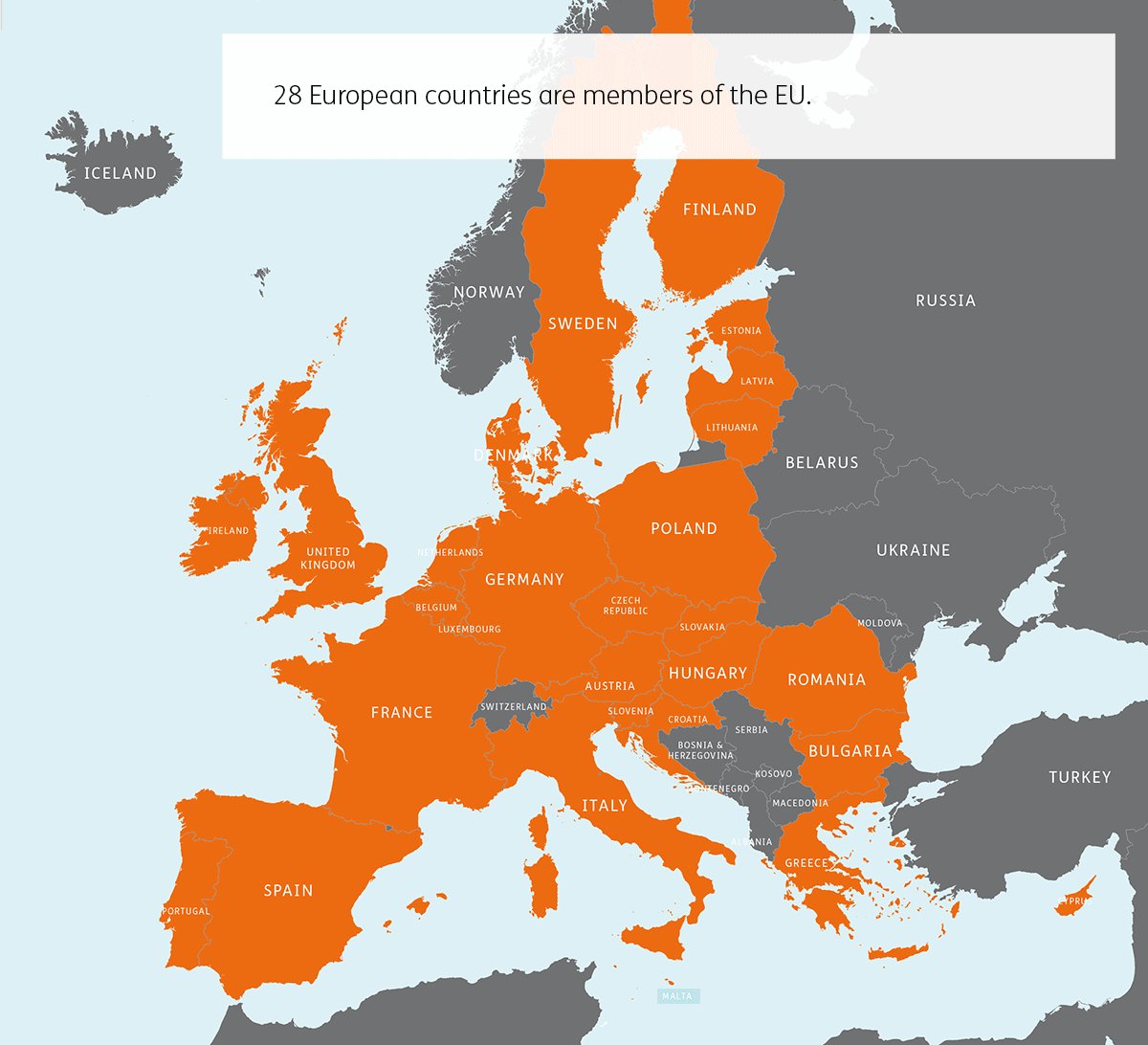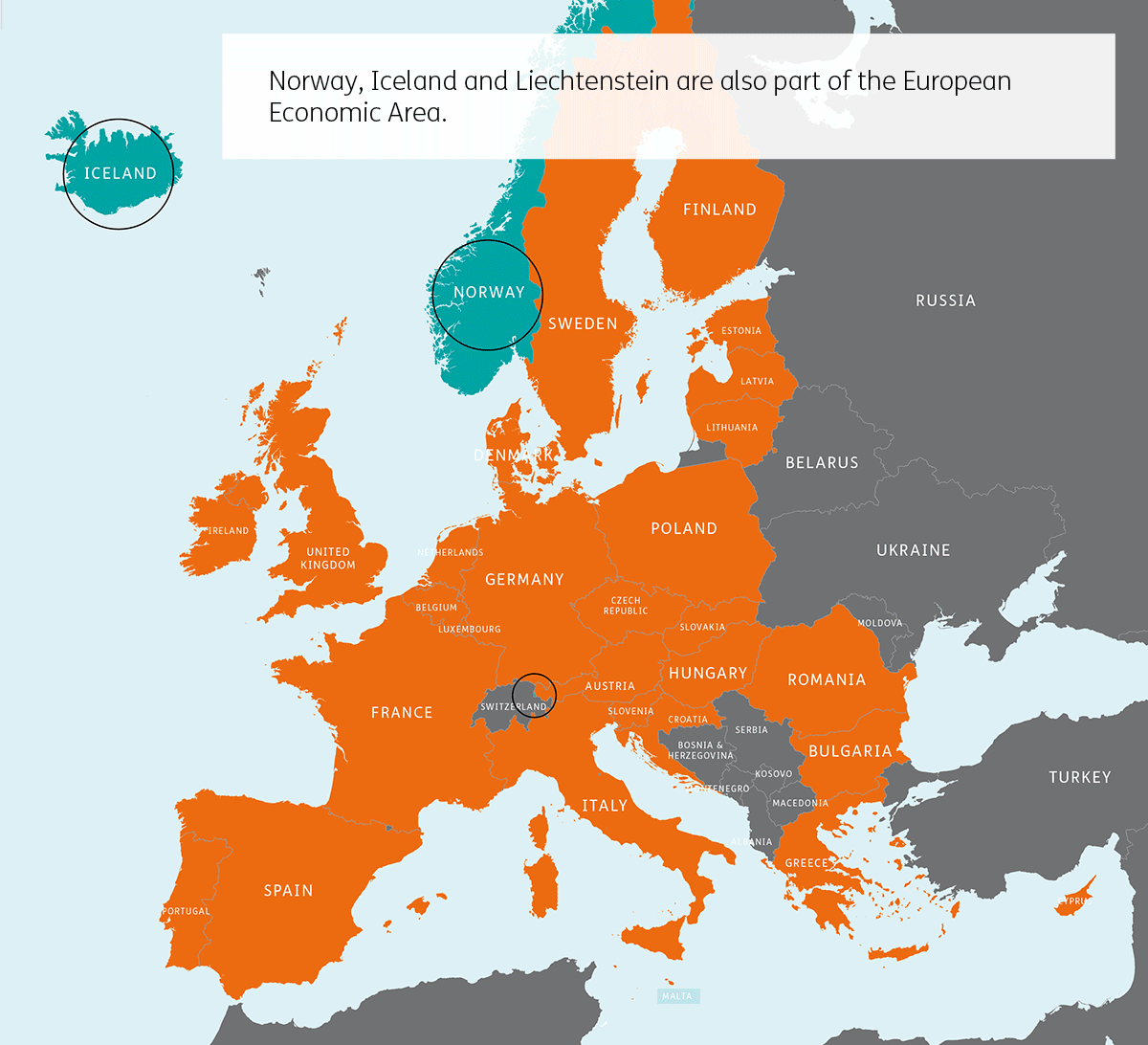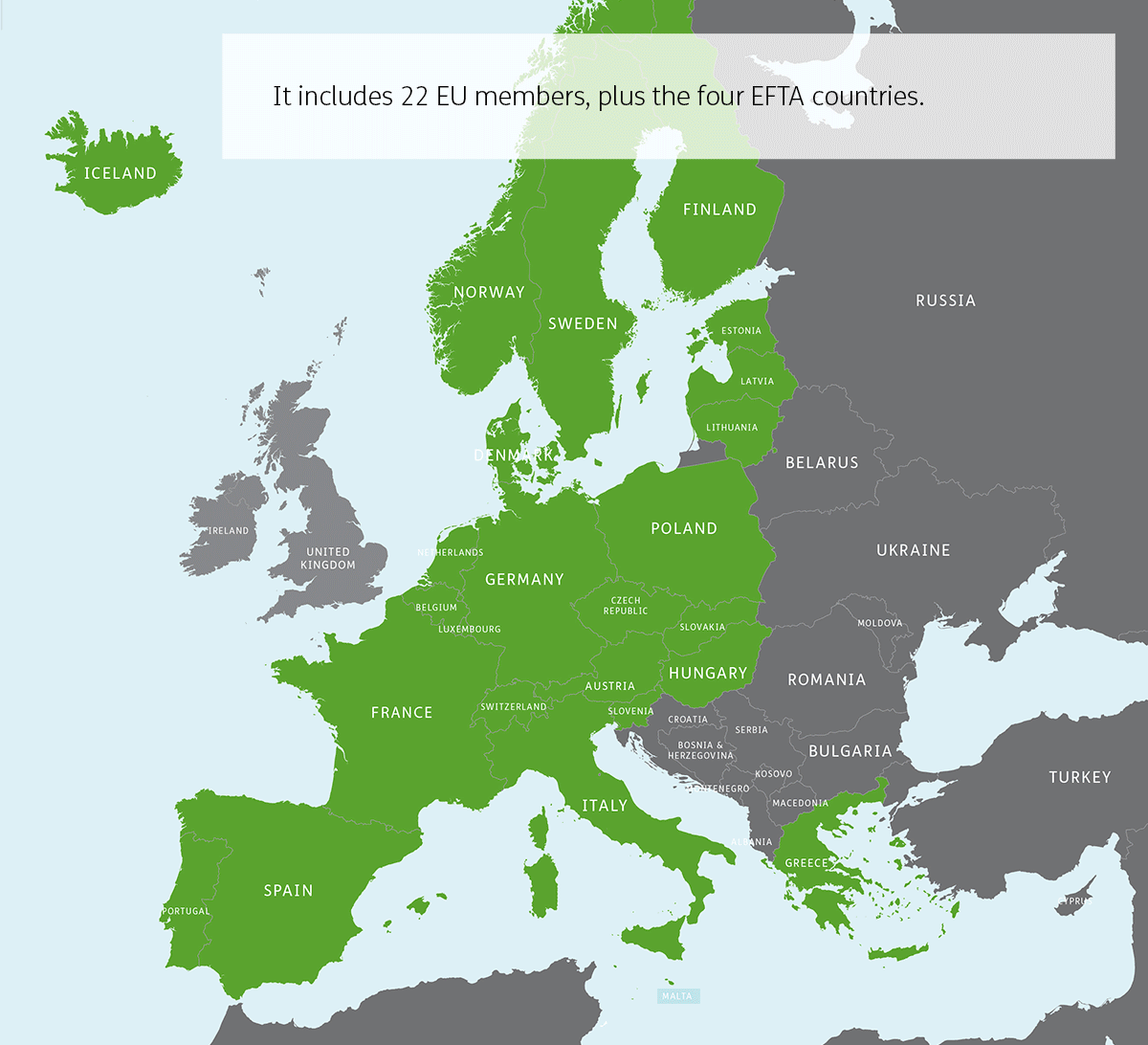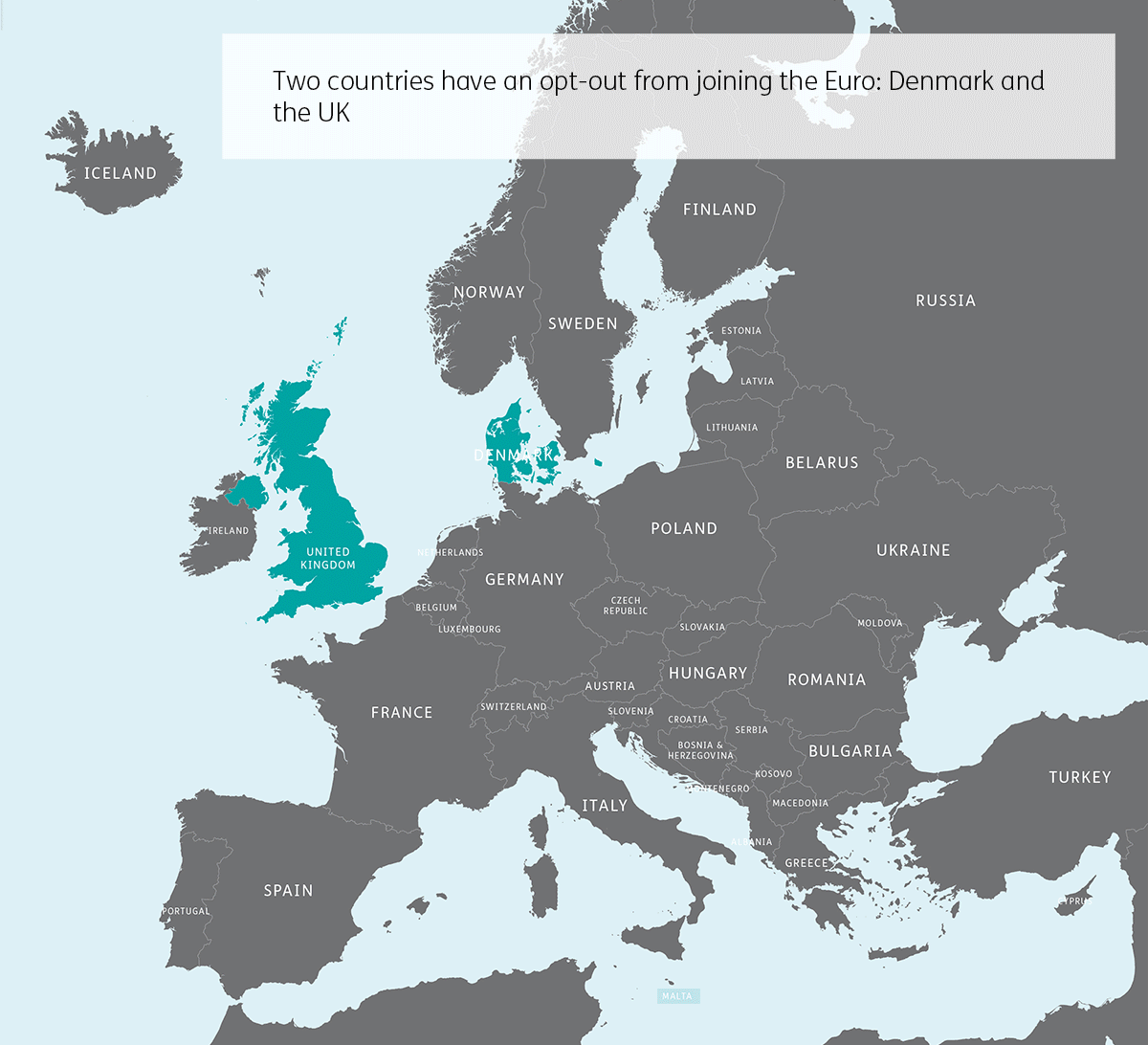
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Republic of Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- United Kingdom
What are the Penalties for Non-Compliance?
In serious breaches of GDPR, a company will be fined either €20 million or 4% of its total global revenue, whichever is the larger amount. This is a staggering amount that can cripple a company if they are not careful to obey the new rules. However, fines will be based on a tiered approach where the fine amount corresponds with the gravity of the breach.
Changes at a Glance
- Increased fines
- Opt-in consent from the user
- Removal of automatic opt-in consent and consent must be easy to withdraw.
- Breach notifications
- Informing affected users and the relevant authority in cases where data is breached.
- In cases of large scale transfers, a Data Protection Officer (DPO) will be assigned to the company.
- Responsibility for transferring data outside of the EU
Companies outside of the EU
GDPR affects all companies that have any sort of interaction with data collection of users in the EU. For example, a US based company such as Starbucks would still have to adhere to GDPR when collecting data from users in France.
Sources
- https://fullfact.org/europe/how-many-countries-in-EU/
- https://gdpr-info.eu/
- https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/law-topic/data-protection_en
Many men go fishing all of their lives not knowing that it is not fish they are after.
— Henry David Thoreau



